Spring Term
Reception
Collecting data
In this topic, children will :
- Know how to use a given to collect data to inform discussions
Year 1
Moving a Robot
In this topic, children will :
- Know what a given command does and to match it with an outcome
- Know how to run a command
- Know that a program is a set of commands a computer can run
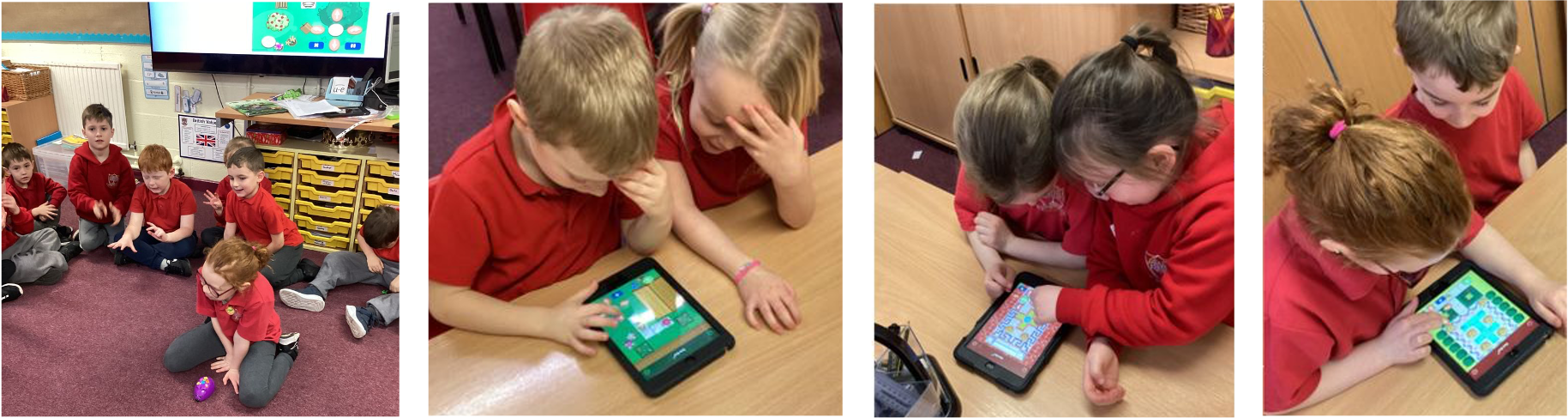

Grouping Data
In this topic, children will :
- Know that information can be presented in different ways
- Know that objects can be counted and identify attributes of an object in on to group them
- collect simple data and add to a table or graph
Year 2
Robot Algorithms
In this topic, children will :
- Know that a series of instructions is a sequence and can be issued before enacted
- Know how logical reasoning can be used to predict the outcome of a program

Pictograms
In this topic, children will :
- Know how a computer program can be used to present information in different ways e.g. tally chart and pictograms
- Use a computer to view data in different formats
- Know objects that have been grouped by attribute and construct a comparison question
- Use pictograms to answer single attribute questions
Year 3
Sequence in Music
In this topic, children will :
- Know that a program starts because of an input
- Know what a sequence is and a program includes sequences of commands and that this is the process
- Know that the order of commands can affect a programs output
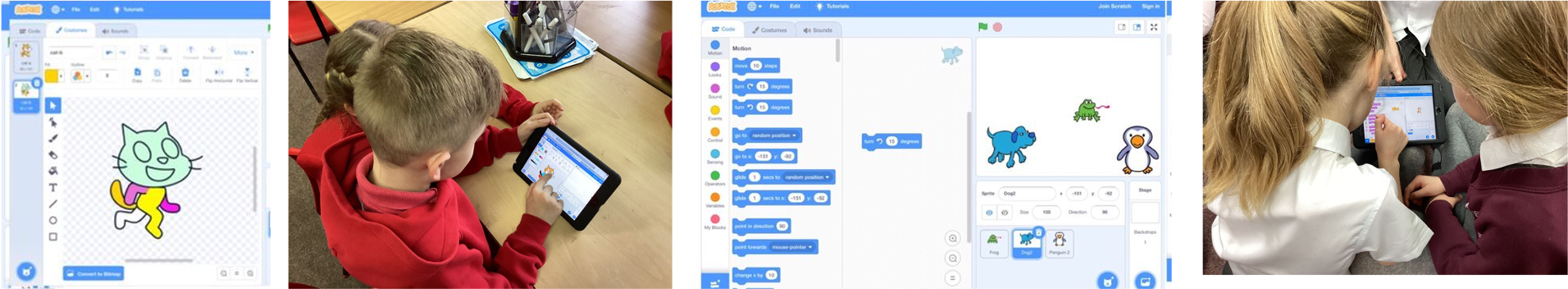
Branching Databases
In this topic, children will :
- Know questions with yes/no answers and data that can be collected to answer questions
- Know an attribute to separate objects into similar sized groups
- Know how to use two levels of branching databases using AND
Year 4
Repetition in Shapes
In this topic, children will :
- Know what 'repeat' means and that repetition is included within sequences
- Know that we can use a lopp command in a program to repeat instructions
- Know that there are count controlled loops and indefinite loops and explain their purpose
- Know the importance of instrcution order in a loop
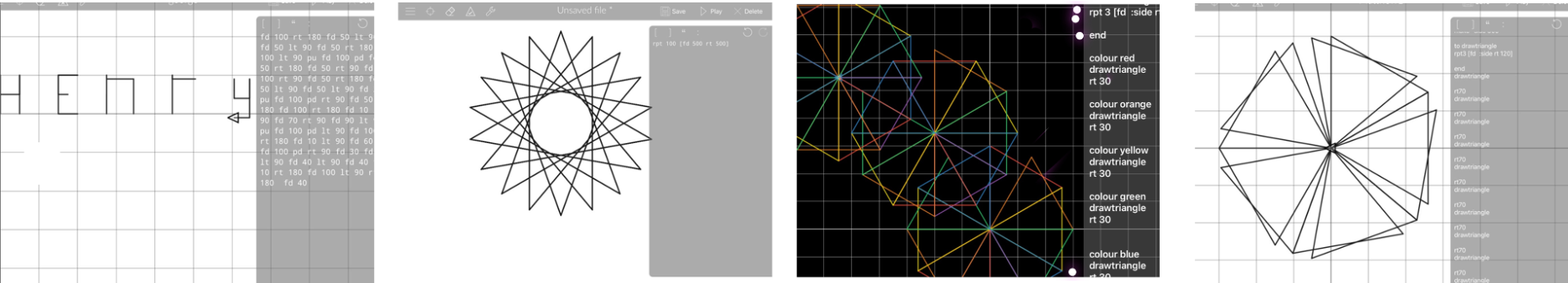
Data Logging
In this topic, children will :
- Know how to use a digital device to collect data automatically
- Know that sensors are input devices and can be used for data collection
- Know that a data logger captures data points from sensors over time
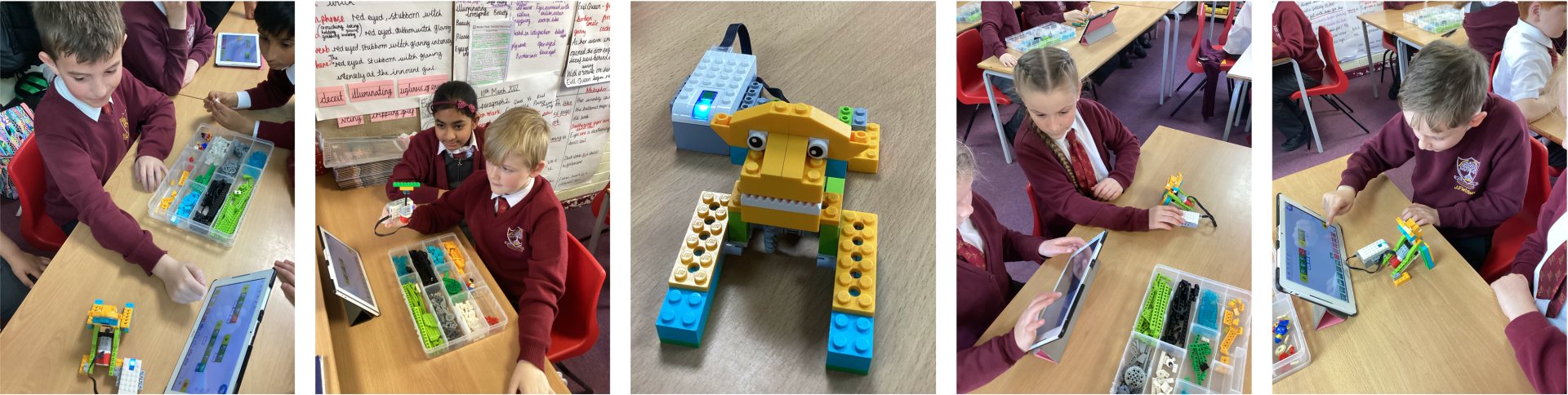
Enrichment - STEM Lego Robotics Workshop
In the STEM workshop, children have been working on their engineering skills. To begin with, children took part in some activities to familiarise themselves with the Lego and programming software. Their next task was to build and program a roaring lion. Children learnt about gears, timers, motor power and simple algorithms to control their models and used practical problem solving skills to create their model.Their learning was then extended to using motion sensors within their algorithm. They then programmed the Lion with movement, sound and backgrounds.

Year 5
Selection in Physical Computing
In this topic, children will :
- Know that a condition can only be true or false
- Know that a count controlled loop contains conditions
- Know that selection can be used to branch the flow of a program
- Know that a loop can be used to repeatedly check whether a condition has been met

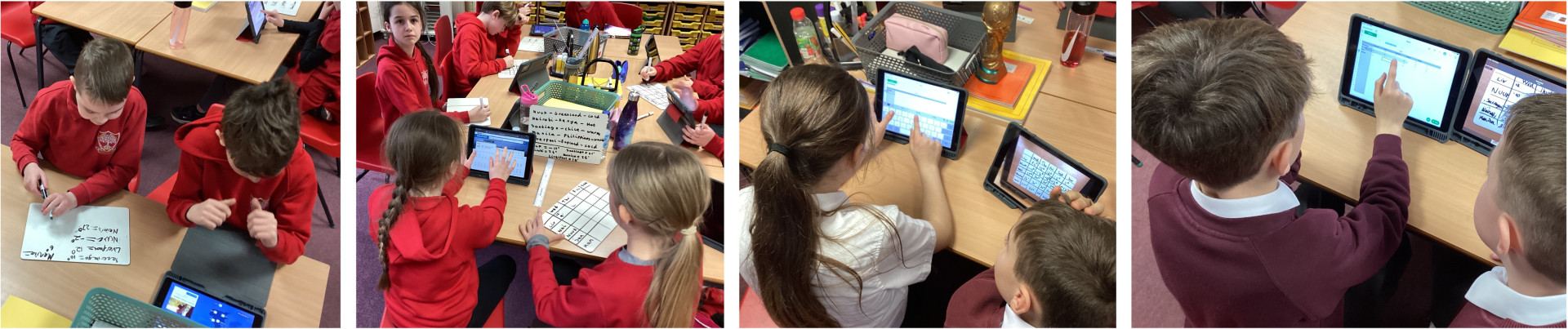
Flat-file Databases
In this topic, children will :
- Know that a computer program can be used to organise data
- Know that toold can be used to select data to answer questions e.g. ordering and filter tools
- Know how 'AND' and 'OR' can be used to refine data selection

Year 6
Variables in Games
In this topic, children will :
- Know variable as something that is changeable and give examples
- Know a program variable as a placeholder in memory for a single value
- Know that the name of a variable need to be unique and is meaningless to the computer
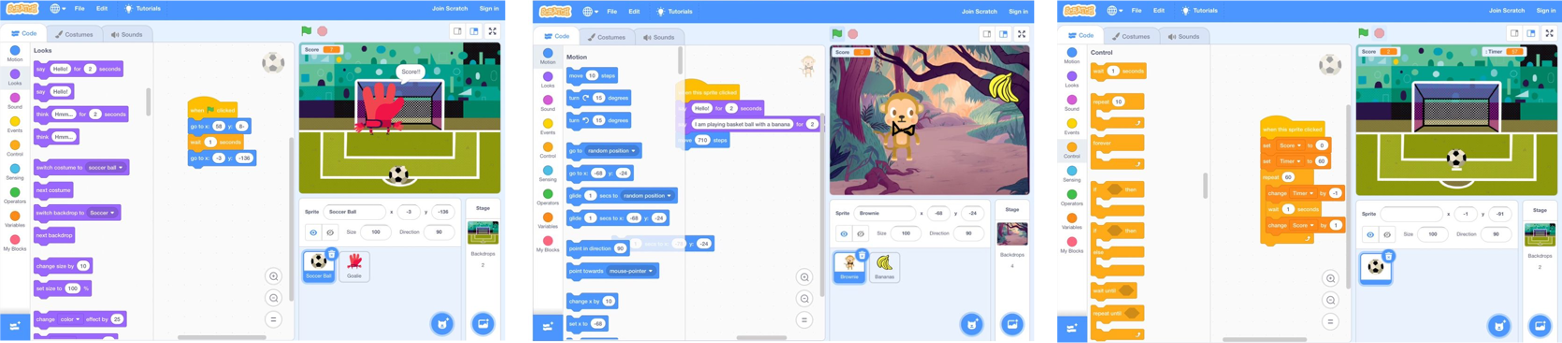
Year 6
Variables in Games
In this topic, children will :
- Know variable as something that is changeable and give examples
- Know a program variable as a placeholder in memory for a single value
- Know that the name of a variable need to be unique and is meaningless to the computer
